

IIRC when it was implemented in the first place, it seemed like lemmy.world had actually been contacted by some stakeholder with a DMCA-style request, even though the community was not actually originating on lemmy.world. Explaining how federation worked to lawyers didn’t matter much and with .world at the time becoming one of the larger and more visible instances that seemed like the best way to avoid the headaches. Initially they defederated with dbzer0 entirely before developing a way to block just the community.
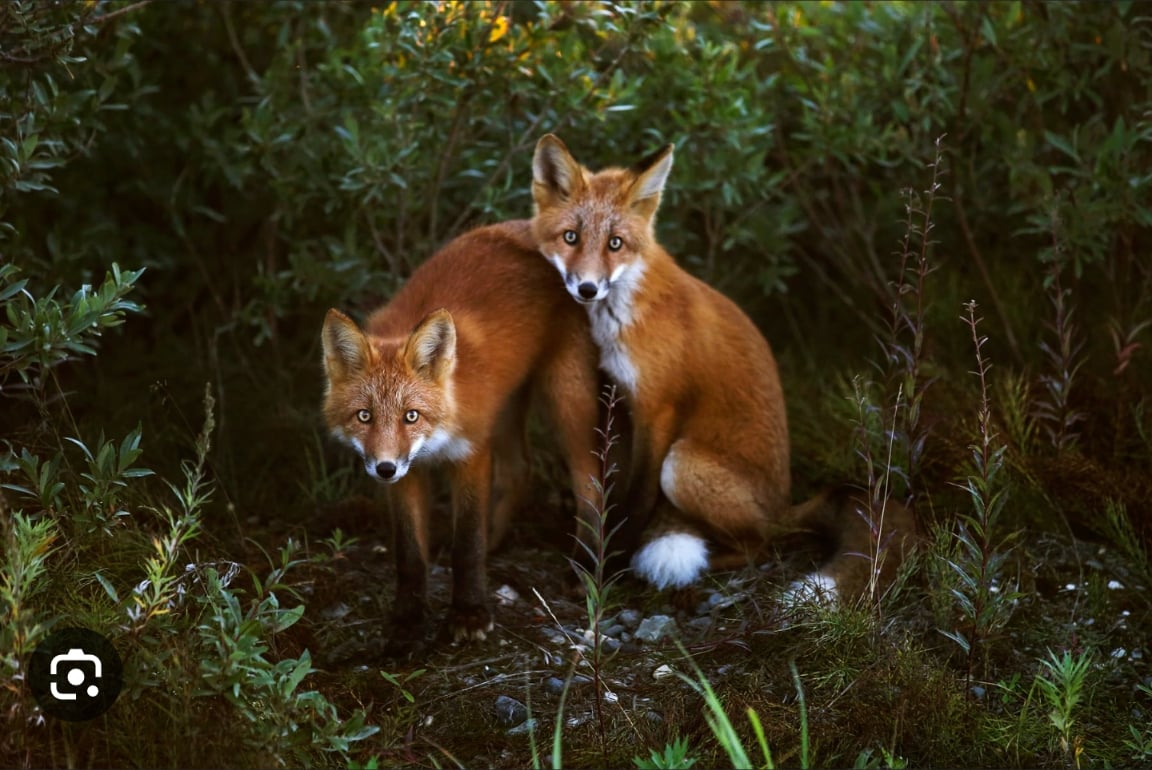







I feel like this should go to some of the programming communities also, but I’m not a programmer so I don’t know where